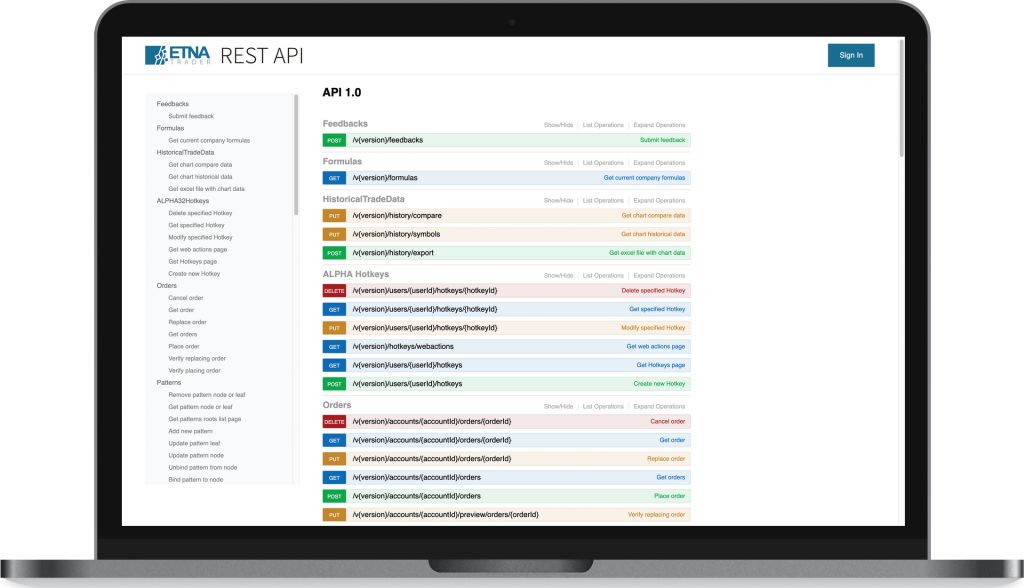
Let’s start by getting a general definition of what a Trade Order Management System (OMS) is before exploring its history, functionality and what’s available in the modern OMS vendors marketplace.
An Order Management System (OMS), is a computer software system used in various industries designed to help manage order entry and processing.
In retail, for example, the OMS would typically take care of customer orders, stock levels, packaging and shipping. It might also need functionality that allows it to synchronize orders over different channels e.g. if a customer orders a product online and picks it up from a physical store – the omni-channel experience.
In online stock trade world Order Management System is responsible for placing orders and trades, making it efficient and cost effective, reporting back to the client in milliseconds; speed that no human could ever hope to achieve.
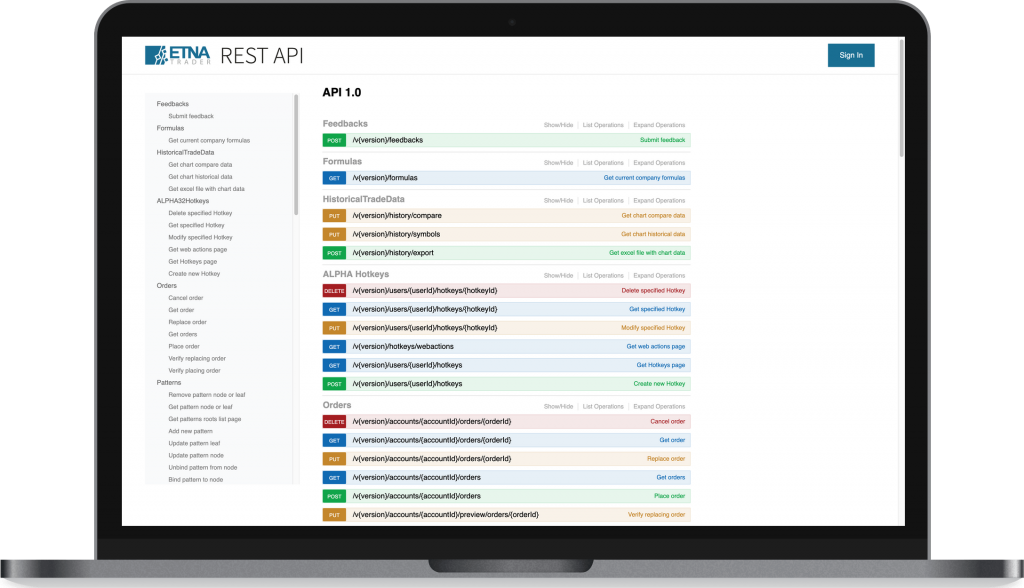
In order to address the growing volumes of stock trade Order Management System was developed. Electronic trading allowed for ever increasing numbers of trades to be executed and it became necessary to have a system in place, capable of managing these trading volumes. This could only be achieved by using technology to manage technology.
The FIX (Financial Information eXchange) protocol was introduced in 1992. FIX facilitated messaging between clients, online broker-dealers, exchanges, and consequently the technology became more versatile. This made the use of an OMS a standard for the industry and essentially everyone started using one.
Orders being executed today are multi-faceted and complex – manual methods of capturing orders, routing and reporting simply wouldn’t work.
In the past, trading was conducted mainly over a national exchange, whereas nowadays an order can be spread over many locations. It’s also necessary to keep track of where and when trades are made – information that must be reported back to the client almost instantaneously.
There are a couple of other terms that crop up in relation when we speak about trade Order Management System, let’s take a deeper dive.
OMS (Order Management System) – Trade Order Management System would traditionally have taken care of the order i.e. managing the order and the trade flow between the client and the various execution venues.
EMS (Execution Management System) – software application to display market data and provide fast access to execution venues for the purpose of transacting orders. The distinction between OMS and EMS have blurred to minimize the number of software applications to maintain and avoid duplicate functionality.
The efforts to combine the functionality of MS and EMS bring us to
OEMS (Order and Execution Management System) – trading software companies have expanded their products’ capabilities over time. Their ultimate goal is to develop an integrated trading “hybrid” or OEMS.
Essentially, we have two parts to a trade on the buy-side – the order and the execution.
EMS concentrates on real-time trading, real-time market data and analytics. Usually an EMS provides functionality across many trading venues such as exchanges, brokerage firms and other trading systems. This functionality may be supported by an algorithm – a set of rules required to complete the tasks. We can view the modern-day trade order management system pretty much as an OEMS.
OMS used in online stock trading today, provide certain functionality which can be summarized as follows:
Trade order management system can be used by both buy-side and sell-side firms, allowing firms to manage the complete lifecycle of a trade and fully automate the process.
Established financial services companies and financial technology firms are using technology to enhance or replace services offered by legacy software vendors. An OMS is a perfect example of the kind of technology that has facilitated this shift in the marketplace.
The proliferation of tech has been the catalyst for financial institutions and tech companies to battle each other for dominance in what is now a highly competitive landscape.
Here are some examples of where a trade order management system might typically be employed:
Online Broker-dealers can automate their trade lifecycle and internal operations using OMS software. Performance can be tracked against pre-defined benchmarks and both client and trader are informed of execution progress and results in real-time.

Robo-Advisor Software
Digital Advisors (Robo-Advisors) – The newly emerged digital advising firms build their unique Customer Experience (CX) on the frontend. This is what makes a difference and draws clients. The backend of a typical digital advisors resembles a lot the one of an online broker-dealer. Highly regulated online brokerage space in the U.S. would not allow much flexibility, and so, instead of reinventing the wheel, such firms private label existing OMS from brokers or technology vendors like ETNA. It saves resources and proved to be efficient over years.
Alternative investment funds (AIF) – alternative investments in classes other than stocks, bonds and cash can also employ an OMS to good effect. Private equity, real estate, commodities, hedge funds and, of course, cryptocurrencies can all maximize efficiency, accountability and reporting by employing OMS tailored to their specific needs.
Portfolio Managers, FinTech firms and robo-advisors benefit from greatly simplified trade management and reduce the risk of an error to minimum.
Trading stock online in our modern world would be impossible without a robust OMS. The huge volume of trades across many different markets (enabled by electronic trading) brought about the need for technology capable of controlling these trades.
Further, clients demand near real-time reporting on trades, again impossible without OMS technology.
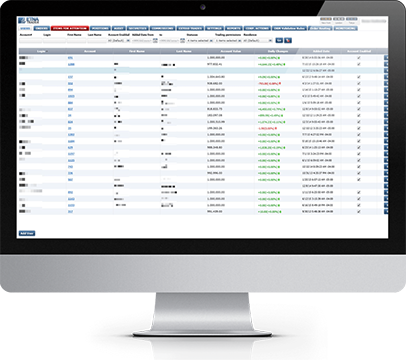
Broker Back Office with OMS
In our modern world OMS are not only bundled with EMS (OEMS) but can also offer seamlessly integrated, multi-asset trading functionality and back office.
Looking to the future, successful vendors will need to keep pace with the ever-accelerating pace of technology.
Technical advances that used to take months or even years to bring to market are being launched almost daily, and vendors who are fleet of foot and equipped to embrace this change rapidly are likely to dominate the OMS technology space.
Interested to learn more about OMS and Stock Trading API we offer? Schedule a call with sales or send us a message.

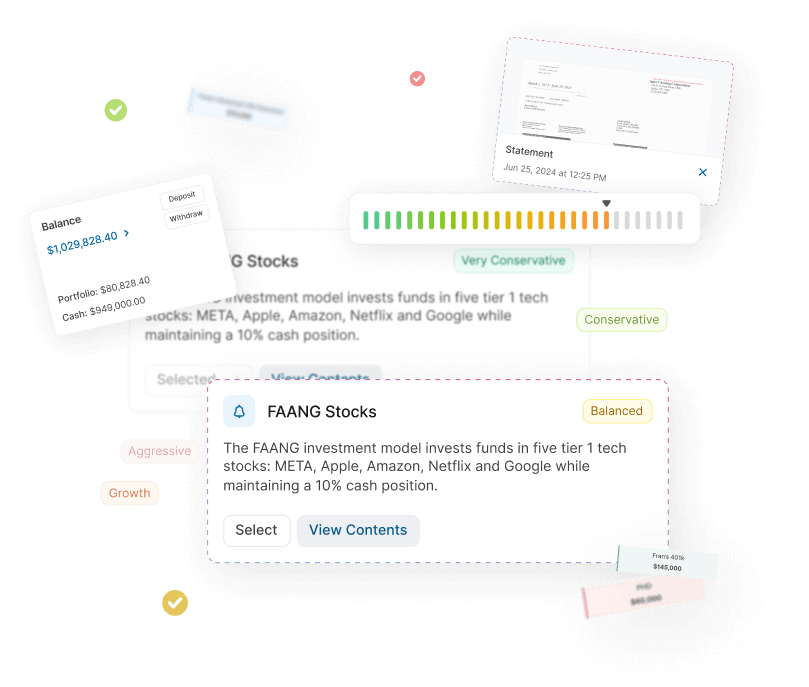
Demo Financial Advisor Software
Manage portfolios with advanced rebalancing and real-time insights.
Access customizable client reports and streamlined compliance tools.
Designed for advisors seeking efficient client and portfolio management.
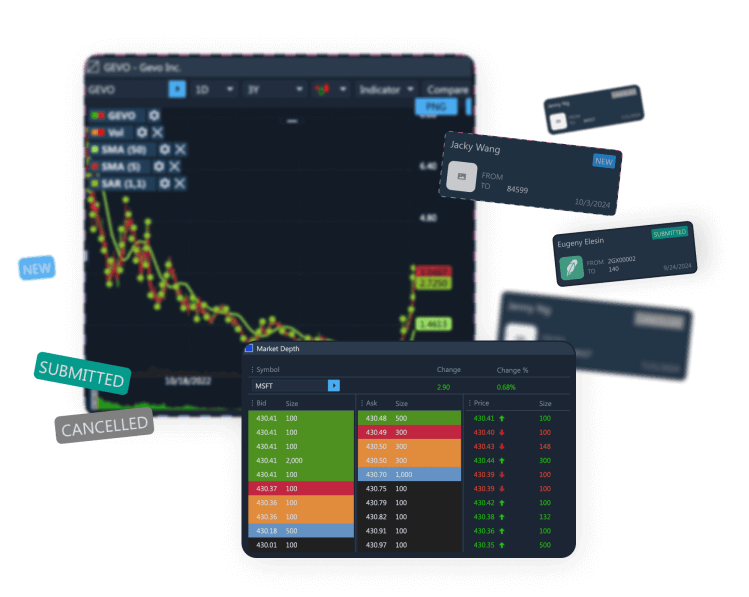
Demo Advanced Trading Platform
Test multi-asset strategies with real-time and historical data.
Analyze market depth, execute complex options, and algorithmic orders.
Ideal for refining strategies and risk management before live trading.

Demo Paper Trading Platform
Practice trading with virtual funds in real market conditions.
Simulate cash, margin, and day-trader accounts to gain experience.
Perfect for honing skills in a risk-free, customizable environment.